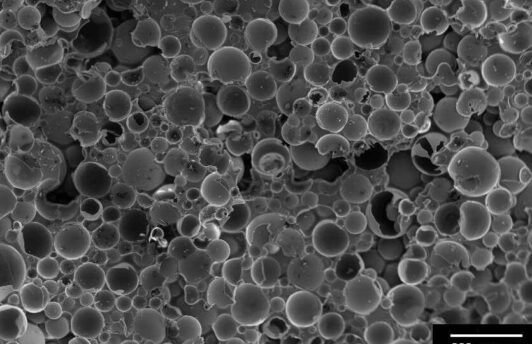
Syntactic foams are complex compounds produced by the incorporation of hollow spherical particles into a polymeric or ceramic matrix. The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) states that synthetic foams have a resin matrix.
The properties of synthetic foam can be largely determined by changing some parameters during their production such as the material of the matrix and fillers, the size of the microspheres, the thickness of their wall and their number – meaning mostly the ratio of their volume with the total volume of foam. The easiness of production is another important advantage of synthetic foams.
Types of Syntactic Foams
- Epoxy synthetic foams are preferred as a matrix material due to their good mechanical properties such as durability and stiffness, small creep and moisture resistance.
- Structural polyamide foams have very good mechanical and electrical properties and their use is great in electronic devices. They are usually combined with silicon spheres.
- Structural polyurethane foams have good compressive strength and high water resistance. They can be soaked in a humid environment for over 10 years and at a water temperature of up to 40oC without significantly degrading their properties.
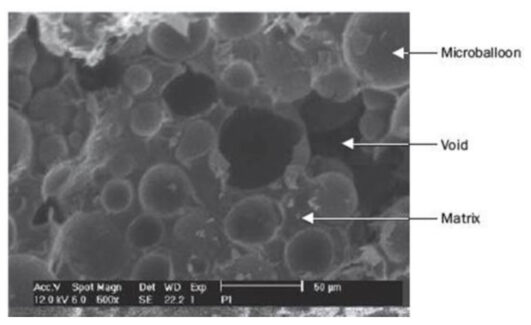
- Polyester synthetic foams in combination with hollow glass microspheres have found great application in the construction of marine vessels and underwater structures due to their buoyancy, non-adsorption of moisture and their low cost.
- Polypropylene is used with hollow glass spheres to have low density, good mechanical and thermal insulation properties.
Syntactic Foams Properties
The spectral distribution for solar irradiance is divided into three regions: UV (200–400 nm—5% of sunlight energy), Visible (400–700nm—45% of sunlight energy) and Near-IR (700–2500 nm—49% of sunlight energy and felt as heat).Approximately 96% of the sunlight’s radiation falls in the 400–2500 nm range, so analysis of the data in this region is of particular interest.Solar reflectance values are typically >80% for coatings formulated specifically as “cool” roof paints, which means they absorb and/or transfer <20% of the incident energy.
Ask for the complete research